Sunhyun Ahn, M.D., Ph.D.
Department of Laboratory Medicine
According to the standards of the United Nations (UN), a society is defined as an aging society when the proportion of people aged 65 and older is more than 14% of the total population. South Korea entered an aging society in 2018. As the aging society progresses, the number of dementia patients is increasing, and as of 2023, it is reported that one out of every ten people aged 65 in South Korea is suffering from dementia (dementia prevalence rate: 10.3%).
Among all dementia cases, Alzheimer dementia accounts for the largest portion at approximately 71.3%, followed by vascular dementia at 16.9% and other types of dementia at 11.8%. When dementia is suspected, cognitive and functional abilities are evaluated through a medical history of the patient and their caregiver, and brain imaging tests (MRI, PET, etc.) are used to investigate the presence of cerebrovascular diseases and brain atrophy for diagnosis.
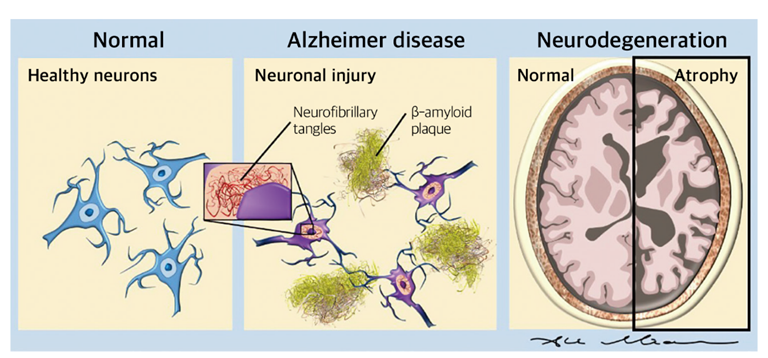
Fig. 1. Pathophysiology of Alzheimer disease by beta-amyloid and tau proteins.
Ref) ALZ imaging-AD pathology and biomarkers
Alzheimer disease is a condition in which beta-amyloid plaques and hyperphosphorylated tau proteins accumulate outside and inside nerve cells, causing the neurons in the brain to degenerate. Currently, the treatment for Alzheimer disease aims to detect the disease early, provide symptomatic treatment, and manage health through activities such as exercise to alleviate symptoms and delay progression. However, brain imaging tests can only confirm significant brain atrophy, so research is ongoing to develop tests that can enable early diagnosis of dementia. Therefore, in this chapter, we would like to explore various Alzheimer disease-related tests that can be conducted using blood or cerebrospinal fluid.
Two types of cerebrospinal fluid Alzheimer disease biomarkers
(β-amyloid 1-42, p-tau, p-tau/Aβ42 ratio) [ECLIA]
As neurodegeneration progresses in dementia patients, beta-amyloid accumulates and amyloid plaques form, but a decrease in beta-amyloid concentration is observed in the cerebrospinal fluid. Additionally, tau proteins associated with neurofibrillary tangles are reported to increase in concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid of dementia patients, both total tau proteins and phosphorylated tau proteins. This is believed to be due to the release of tau proteins from dying brain nerve cells in dementia patients, leading to an increase in the cerebrospinal fluid. The testing method utilizing this involves measuring the levels of CSF-Aβ and CSF-tau/p-tau. Currently, the average concentrations of beta-amyloid and tau proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid of normal individuals and dementia patients are known, making the development of dementia diagnostic markers using this method the most active field.
The p-tau/Aβ42 ratio cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis has been shown to correlate with amyloid PET by approximately 90%, suggesting that it could be an alternative to PET in Alzheimer disease diagnosis. However, a drawback of using CSF for dementia diagnosis is that it requires an invasive procedure of lumbar puncture to obtain the CSF.
Table 1. Reference range of two biomarkers for Alzheimer disease in cerebrospinal fluid
Test item | Reference rage |
p-tau/Abeta42 ratio | ≤ 0.023 |
β-amyloid (1-42) (Abeta42) | > 1030 pg/mL |
Phospho-tau (181P) (p-tau) | ≤ 27 pg/mL |
Oligomerized amyloid β [ECLIA]
This test quantitatively measures beta-amyloid oligomers in the plasma (heparin) of patients suspected of Alzheimer disease using electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA). Beta-amyloid is formed from soluble beta-amyloid monomers (Aβ monomer), dimers, oligomers, and fibrils derived from amyloid precursor protein (APP), ultimately forming insoluble plaques. Since beta-amyloid monomers are non-toxic and can be found in normal individuals, a sandwich ELISA method is used to selectively detect toxic oligomers by overlapping the antigen recognition sites of the capture/detection antibodies that react to the antigen.

Fig. 2. Reference range for amyloid beta testing in Alzheimer disease
Human amyloid β [ELISA]
Beta-amyloid is a peptide composed of 40 or 42 amino acids associated with Alzheimer disease, with plaques mainly known to consist of Aβ1-42, as well as Aβ1-40, Aβ4-38, and others. Many studies have reported an increase in the concentration of Aβ1-40 in the cerebrospinal fluid and blood of Alzheimer patients, as well as a decrease or mild increase in the concentration of Aβ1-42, resulting in a decrease in the ratio of Aβ1-42/Aβ1-40. This test measures the concentration of beta-amyloid of various sizes using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Table 2. Reference range for human amyloid beta testing
Unit: pg/mL
Aβ1-40 | Aβ1-42 | 42/40 ratio | |
Male | 128.38~297.44 | 2.13~12.64 | 0.010~0.080 |
Female | 125.38~332.23 | 2.50~22.16 | 0.010~0.110 |
APOE (apolipoprotein E) genotype [Real-time PCR]
Apolipoprotein E (APOE) is a apolipoprotein mainly produced in the liver, which transports cholesterol to nerve cells in the central nervous system. The APOE gene is located on chromosome 19 and has three allelic variants: E2, E3, and E4 (APOE e2, APOE e3, APOE e4). E4 in particular binds to very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and is involved in lipid transport, glucose metabolism, brain vascular function, and tau-mediated neurodegenerative processes, showing relevance to various cerebrovascular and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer disease. However, Alzheimer dementia is influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors, so even with a specific APOE genotype, the disease may not develop. Therefore, it can be used as a diagnostic support test for symptomatic patients.
Table 3. Example of APOE gene test results
Risk of Alzheimer disease | Low risk group | Moderate risk group | High risk group | |||
APOE genotype | E2/E2 | E2/E3 | E3/E3 | E2/E4 | E3/E4 | E4/E4 |
○ | ||||||
Alzheimer disease not only affects the patient's daily life with cognitive impairment, but also impacts the lives of the entire family. Various testing methods are known to help detect dementia early and delay its progression. In addition, efforts are being made not only in Korea but globally to research treatments for Alzheimer disease and develop early diagnostic methods, so it is expected that testing methods with improved sensitivity and specificity will continue to be developed in the future.
Reference
01. Querfurth HW and LaFerla FM. Alzheimer's disease. Engl J Med. 2010 Jan 28;362(4):329-44.
02. Barbara J Snider, Anne M Fagan, Catherine Roe, Aarti R Shah, Elizabeth A Grant, Chengjie Xiong, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and rate of cognitive decline in very mild dementia of the Alzheimer type. Arch Neurol. 2009;66(5):638-645.
03. The Ministry of Korea Health and Welfare, The Korea New Health Technology Assessment Committee. nHTA Report HTA-2020-27 Oligomeric amyloid beta protein [ELISA]. 2020.
04. Saido T.C., Iwatsubo T., Mann D.M.A., Shimada H., Ihara Y., Kawashima S. Dominant and differential deposition of distinct β-amyloid peptide species, AβN3(pE), in senile plaques. Neuron. 1995 Feb;14(2):457-66.
05. Yu Yamazaki, Na Zhao, Thomas R Caulfield, Chia-Chen Liu, Guojun Bu. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: pathobiology and targeting strategies. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019 Sep;15(9):501-518.
Test Information
GC Labs code | Test item |
G323 | |
S875 |

